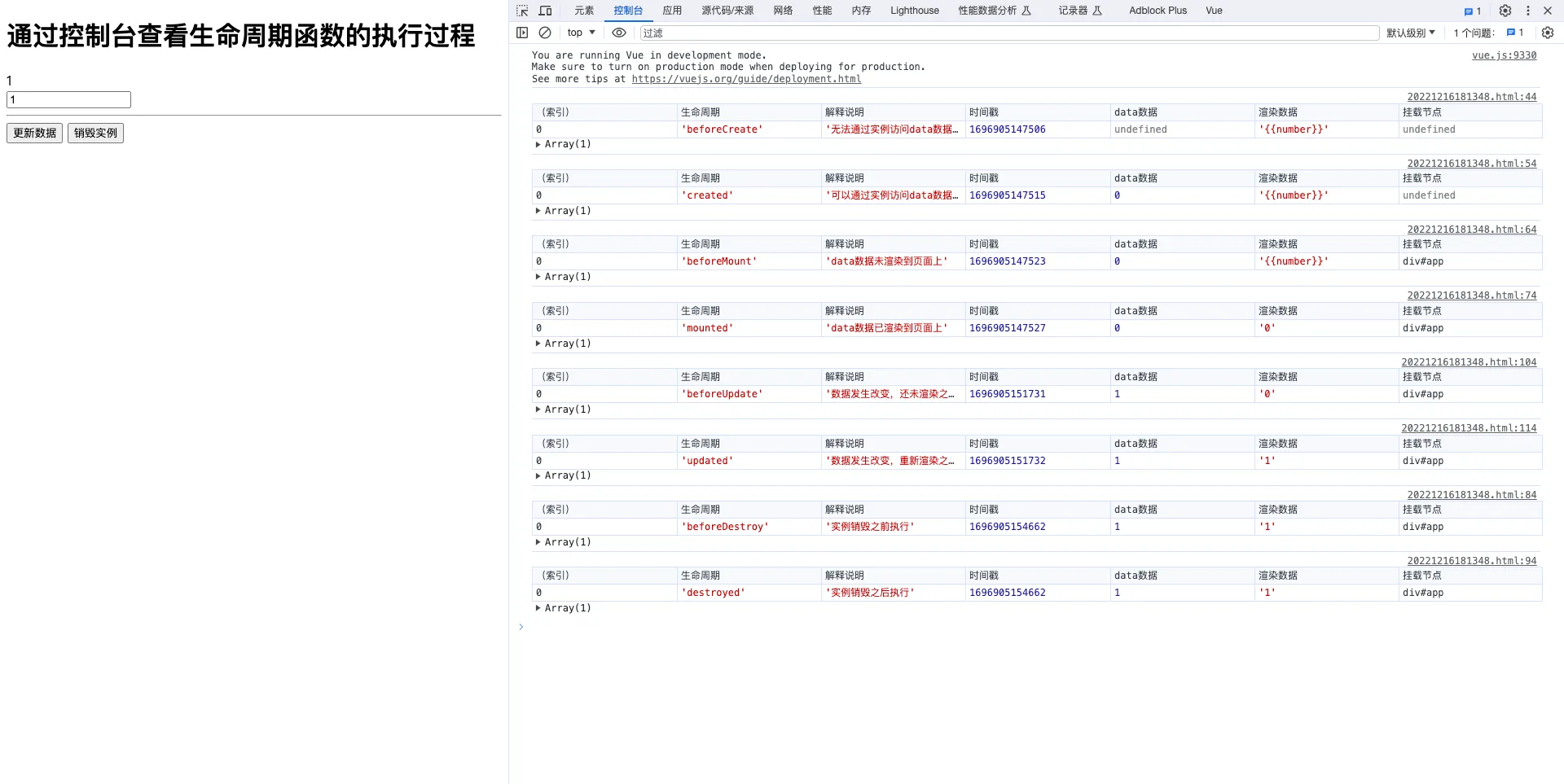
本章将快速讲解部分 Vue 基础语法,通过 TodoList 功能的编写,在熟悉基础语法的基础上,扩展解析 MVVM 模式及前端组件化的概念及优势。
2.1 课程学习方法
基础部分,看完视频教程,找到官网对应文档进行阅读吸收。
实战部分,根据视频从头到尾把代码敲写出来。
2.2 hello world
2.2.1 兼容性
Vue 不支持 IE8 及以下版本,因为 Vue 使用了 IE8 无法模拟的 ECMAScript 5 特性。但它支持所有兼容 ECMAScript 5 的浏览器。
2.2.2 开发版和生产版本
- 开发版包含完整的警告和调试模式
- 生产版删除了警告(33.30KB min+gzip),体积更小,加载更快
2.2.3 hello world 效果的实现
原生实现方法:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>去哪儿</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var app = document.getElementById("app");
app.innerText = "hello word"
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Vue实现方法:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>去哪儿</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- {{}} 差值表达式 -->
<div id="app">{{content}}</div>
<script src="../static/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({ // vue 实例
el:"#app", // 实例管理的区域
data:{ // 定义数据
content:"hello world"
}
})
// setTimeout(function(){
// app.$data.content = "bye world"
// },2000)
</script>
</body>
</html>
vue书写代码,无需在把时间放在DOM操作上面,只需关注数据即可。
2.3 开发TodoList(v-model、v-for、v-on)
案例参考:http://todolist.cn
用到的指令:v-for、v-on、v-model
2.3.1 循环数据:v-for
v-for 指令可以绑定数组的数据来渲染一个项目列表
<div id="app-4">
<ol>
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{{ todo.text }}
</li>
</ol>
</div>
var app4 = new Vue({
el: '#app-4',
data: {
todos: [
{ text: '学习 JavaScript' },
{ text: '学习 Vue' },
{ text: '整个牛项目' }
]
}
})
输出结果:
1. 学习 JavaScript
2. 学习 Vue
3. 整个牛项目
2.3.1 绑定事件:v-on
处理用户输入
为了让用户和你的应用进行交互,我们可以用 v-on 指令添加一个事件监听器,通过它调用在 Vue 实例中定义的方法:
<div id="app-5">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="reverseMessage">反转消息</button>
</div>
var app5 = new Vue({
el: '#app-5',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue.js!'
},
methods: {
reverseMessage: function () {
this.message = this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})
点击后输出结果:
!sj.euV olleH
注意在 reverseMessage 方法中,我们更新了应用的状态,但没有触碰 DOM——所有的 DOM 操作都由 Vue 来处理,你编写的代码只需要关注逻辑层面即可。
2.3.3 数据双向绑定:v-model
Vue 还提供了
v-model指令,它能轻松实现表单输入和应用状态之间的双向绑定。
<div id="app-6">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div>
var app6 = new Vue({
el: '#app-6',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})
2.3.4 方法定义在 vue 实例的 methods 里面
几个关键字
app.$data.inputValue // 获取 data 中的数据
没有操作DOM,一直在操作数据
MVVM 设计模式
效果的实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>todolist</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="inputValue">
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button>
<ul>
<!-- 循环data中的list数据,循环的每一项放在item里面 -->
<li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../static/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data: {
list:[],
inputValue:''
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick: function(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4 MVVM模式
2.4.1 MVP
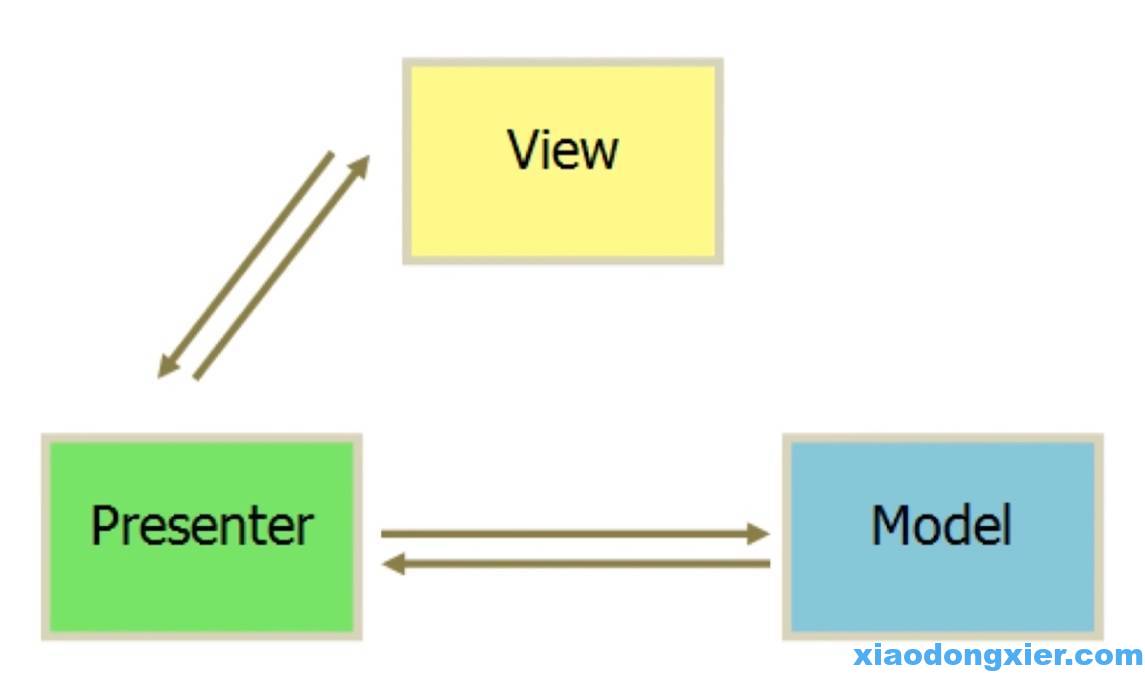
jQuery 面向 DOM 进行开发
M模型层(ajax请求) V视图层 P控制器
MVP todolist
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>jQuery todolist</title>
<script src="../static/jquery/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="" id="input">
<button id="btn">提交</button>
<ul id="ulElement"></ul>
<script>
function Page(){}
$.extend(Page.prototype,{ // $.extend
init: function(){
this.bindEvents()
},
bindEvents: function(){
var btn = $("#btn");
btn.on("click",$.proxy(this.handleBtnClick,this)) // $.proxy
},
handleBtnClick:function(){
var inputValue = $("#input");
var ulElement = $("#ulElement");
ulElement.append(`<li>${inputValue.val()}</li>`)
inputValue.val("")
}
})
var page = new Page()
page.init()
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4.2 MVVM
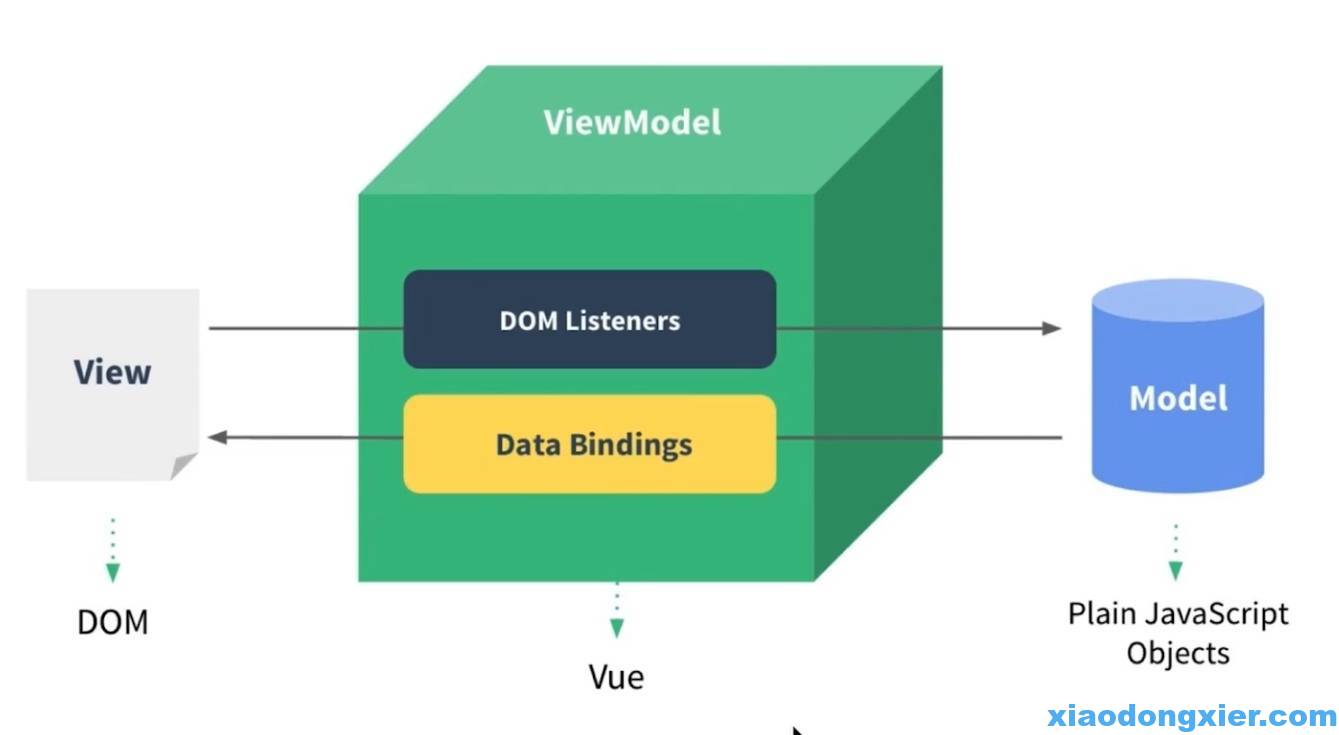
Vue 面向数据进行编程
M层负责存储数据 V层负责显示数据 VM层(Vue内置的) 没有P层
MVVM todolist
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>todolist</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="inputValue" v-on:keyup.enter="enterDown">
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button>
<ul>
<!-- 循环data中的list数据,循环的每一项放在item里面 -->
<li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../static/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data: {
list:[],
inputValue:''
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick: function(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
},
enterDown: function(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
因为无需操作 DOM,Vue 开发要比 jQuery 开发减少 30% 以上的代码量。
2.4.3 附加
- 数据绑定的实现原理
- 虚拟DOM机制,
- 相关源码学习
2.5 前端组件化
一个大型的项目,业务逻辑可能非常的复杂,合理的把页面拆分成一个个组件可以使页面更容易维护
每一个组件就是页面上的一个区域
2.6 使用组件化思想修改 TodoList
因为组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,所以它们与
new Vue接收相同的选项,例如data、computed、watch、methods以及生命周期钩子等。仅有的例外是像el这样根实例特有的选项。
通常一个应用会以一棵嵌套的组件树的形式来组织:

例如,你可能会有页头、侧边栏、内容区等组件,每个组件又包含了其它的像导航链接、博文之类的组件。
为了能在模板中使用,这些组件必须先注册以便 Vue 能够识别。这里有两种组件的注册类型:全局注册和局部注册。至此,我们的组件都只是通过 Vue.component 全局注册的:
Vue.component('my-component-name', {
// ... options ...
})
全局注册的组件可以用在其被注册之后的任何 (通过 new Vue) 新创建的 Vue 根实例,也包括其组件树中的所有子组件的模板中。
到目前为止,关于组件注册你需要了解的就这些了,如果你阅读完本页内容并掌握了它的内容,我们会推荐你再回来把组件注册读完。
2.6.1 全局组件使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>todolist</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="inputValue">
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button>
<ul>
<todo-item v-bind:content="item" v-for="item in list"></todo-item>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../static/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 全局组件,可以直接在模板里使用
Vue.component("TodoItem",{
props:['content'],
template:"<li>{{content}}</li>" // 模板里面用插值表达式
})
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data: {
list:[],
inputValue:''
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick: function(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.6.2 数据传递
Prop 是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义 attribute。当一个值传递给一个 prop attribute 的时候,它就变成了那个组件实例的一个属性。
一个组件默认可以拥有任意数量的 prop,任何值都可以传递给任何 prop。
v-bind –>子组件传入绑定值
2.6.3 局部组件使用
全局注册
到目前为止,我们只用过 Vue.component 来创建组件:
Vue.component('my-component-name', {
// ... 选项 ...
})
这些组件是全局注册的。也就是说它们在注册之后可以用在任何新创建的 Vue 根实例 (new Vue) 的模板中。比如:
Vue.component('component-a', { /* ... */ })
Vue.component('component-b', { /* ... */ })
Vue.component('component-c', { /* ... */ })
new Vue({ el: '#app' })
<div id="app">
<component-a></component-a>
<component-b></component-b>
<component-c></component-c>
</div>
在所有子组件中也是如此,也就是说这三个组件在各自内部也都可以相互使用。
局部注册
全局注册往往是不够理想的。比如,如果你使用一个像 webpack 这样的构建系统,全局注册所有的组件意味着即便你已经不再使用一个组件了,它仍然会被包含在你最终的构建结果中。这造成了用户下载的 JavaScript 的无谓的增加。
在这些情况下,你可以通过一个普通的 JavaScript 对象来定义组件:
var ComponentA = { /* ... */ }
var ComponentB = { /* ... */ }
var ComponentC = { /* ... */ }
然后在 components 选项中定义你想要使用的组件:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'component-a': ComponentA,
'component-b': ComponentB
}
})
对于 components 对象中的每个属性来说,其属性名就是自定义元素的名字,其属性值就是这个组件的选项对象。
注意局部注册的组件在其子组件中*不可用*。例如,如果你希望 ComponentA 在 ComponentB 中可用,则你需要这样写:
var ComponentA = { /* ... */ }
var ComponentB = {
components: {
'component-a': ComponentA
},
// ...
}
或者如果你通过 Babel 和 webpack 使用 ES2015 模块,那么代码看起来更像:
import ComponentA from './ComponentA.vue'
export default {
components: {
ComponentA
},
// ...
}
注意在 ES2015+ 中,在对象中放一个类似 ComponentA 的变量名其实是 ComponentA: ComponentA 的缩写,即这个变量名同时是:
- 用在模板中的自定义元素的名称
- 包含了这个组件选项的变量名
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>todolist</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="inputValue" maxlength="11">
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button>
<ul>
<todo-item
v-bind:content="item"
v-for="item in list">
</todo-item>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../static/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 局部组件,需要注册才能正常使用
var TodoItem = {
props:['content'],
template:"<li>{{content}}</li>" // 模板里面用插值表达式
}
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
components: {
TodoItem:TodoItem
},
data: {
list:[],
inputValue:''
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick: function(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.7 简单的组件间传值
本节的几个关键字
index,$emit,v-bind
2.7.1 父组件向子组件传值
通过 v-bind 方式进行数据的传递,
父组件可以使用 props 把数据传给子组件。子组件通过 props 进行接收
2.7.2 子组件向父组件传值
子组件可以使用 $emit 触发父组件的自定义事件。
通过事件触发,向上一层触发事件
子组件触发的事件,恰好父组件在监听,然后带出子组件传递出来的内容
案例预览
vm.$emit( event, arg ) //触发当前实例上的事件
vm.$on( event, fn ); //监听event事件后运行 fn;
子传父案例(点击删除 list)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>子组件向父组件传值</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="inputValue">
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button>
<ul>
<todo-item
v-bind:content="item"
v-bind:index="index"
v-for="(item,index) in list"
v-on:delete="handleBtnDelete">
</todo-item>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../static/vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var TodoItem = {
props:['content','index'],
template:"<li @click='handleItemClick'>{{content}}</li>",
methods: {
handleItemClick: function() {
this.$emit("delete",this.index)
}
}
}
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
components: {
TodoItem:TodoItem
},
data: {
list:[],
inputValue:''
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick: function(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
},
handleBtnDelete: function(index){
this.list.splice(index,1)
// console.log(idnex) 会报错是为什么呢?
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
疑问:关于 index 打印报错是为什么呢?alert能正确弹出下标,但是 console.log 却报错是为什么呢?

2.7.3 v-bind简写
v-bind:content="item"==:content="item"
<todo-item v-bind:content="item"></todo-item>
等同于
<todo-item :content="item"></todo-item>
2.8 本章小结
2.8.1 总结
v-model v-bind(简写:':') v-on(简写:'@') v-for
- 数据双向绑定
- 父子组件传值
- todolist
2.8.1 补充学习
阅读理解官网 介绍 部分内容
条件
案例 预览
控制切换一个元素是否显示也相当简单:
<div id="app-3">
<p v-if="seen">现在你看到我了</p>
</div>
var app3 = new Vue({
el: '#app-3',
data: {
seen: true
}
})
继续在控制台输入 app3.seen = false,你会发现之前显示的消息消失了。
这个例子演示了我们不仅可以把数据绑定到 DOM 文本或 attribute,还可以绑定到 DOM 结构。此外,Vue 也提供一个强大的过渡效果系统,可以在 Vue 插入/更新/移除元素时自动应用过渡效果。